Part Zero
Clean disks!
Defregment disks!
Check them for errors!
Make sure windows drive has enough space!
Part One
This method will produce an ISO image which can be compared to any original Windows 10 ISO you download from Microsoft. It gives a clean Windows installation when used, with the latest build (depending of course on if you upgraded to latest Fast Ring build before making the ISO).
ISO created will include no user profile folders, personal user data and files.
This is the recommended method if you simply need a clean, standard Windows 10 ISO install media.
1.1) Clean install Windows on your reference machine (physical or vm) with the latest available build install media1.2) When on Desktop, opt in for Insider Fast Ring build upgrades (tutorial), restart1.3) Let the vm or physical machine stay on, it will soon pick the latest Fast Ring build upgrade (although often getting upgrade immediately, it in some cases might take up to 48 hours online time. The less you let machine to be off and offline, the sooner you will get the upgrade).When upgrade has been found let Windows Update to download and prepare it and finally restart letting Windows to be upgraded. If using Hyper-V, create a checkpoint when upgrade has been done and you are back on desktop
Alternatively, if you already have a physical or virtual machine upgraded to the latest build, the build you want to make an ISO image from, you can skip steps 1.1 to 1.3 above and use this existing Windows installation instead.
If doing so, please notice that you should first uninstall all installed software except native Windows 10 apps.
1.4) Restart Windows in Audit Mode with following command in Command Prompt:
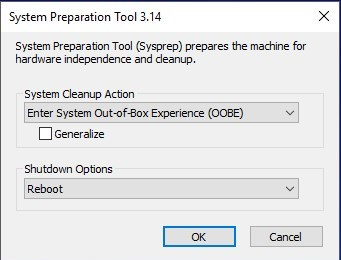 Leave it open for now.1.6) Delete all existing user accounts and their user profile data (Option One in this tutorial), uninstall all possibly installed third party software1.7) You are at the moment signed in using Windows built-in administrator account. In File Explorer, open C:\Users\Administrator folder and check that all user folders are empty deleting all possibly found content
Leave it open for now.1.6) Delete all existing user accounts and their user profile data (Option One in this tutorial), uninstall all possibly installed third party software1.7) You are at the moment signed in using Windows built-in administrator account. In File Explorer, open C:\Users\Administrator folder and check that all user folders are empty deleting all possibly found content1.8) Run Disk Clean-up, selecting and removing everything possible (tutorial).When done, check the C: drive. If folder Windows.old exists after Disk Clean-Up, follow instructions in this tutorial to remove it: Windows.old Folder – Delete in Windows 10
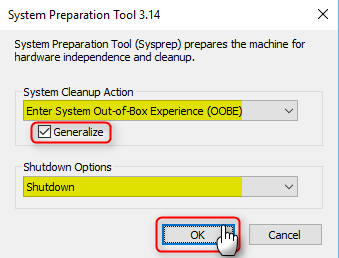
1.9) When clean-up is done, in Sysprep dialog select System Cleanup Action: Enter System Out-of-Box Experience (OOBE), select Shutdown Options: Shutdown, select (tick the box) Generalize, click OK:
1.10) Sysprep will now prepare Windows, shutting down machine when done:

1.11) If using Hyper-V vm, create a checkpoint when Windows has shut down after Sysprep. Continue from Part Four below
Part Two
Custom W10 ISO with pre-installed software & pre-set user accounts
Capturing install.wim from an existing installation only works on computers / virtual machines where all system elements and user accounts are located on Windows system partition C:.
If any data is located on another drive, even a single file or folder be it a Save Game folder of a game or relocated Documents folder, OneDrive located on another drive and so on, the install.wim can be created but it will be corrupt. The ISO created from it will not install Windows.
Use this method in Part Two only if your complete installation is on C: drive. You can for instance clean install Windows on a reference computer, create the user accounts you want to have, install your preferred software and so on, and only move system elements to other drives after you have installed Windows using your custom ISO.
This method will produce an ISO image which can be compared to any original Windows 10 ISO you download from Microsoft, apart from the fact that it already contains pre-installed software according to your choice and pre-set user accounts each which its settings, customisations and personalisations.
ISO created will include all user profile folders and personal user files.
As the settings and user accounts are pre-set, installation using this ISO will be faster than using a standard ISO because Windows don’t have to run OOBE setup. Shorter install time, with pre-installed software (depending on the amount of personal files in user folders).
This method is recommended if and only when the ISO will never be used to install Windows on any other computer than your own computers.
Recommended: To speed up capturing install.wim in Part Four, and make installation using your customised ISO faster, move as much of personal user content from each profile folder to an external drive before proceeding. When ready, move the data back to respective user profiles.
2.1) Create all user accounts you want to, signing once in to each account to create profile folders. Sign out from all new user accounts, sign in to your main local admin account2.2) Install / uninstall software as you prefer, update Windows fully.
2.3) Run Extended Disk Clean-up, selecting and removing everything possible (tutorial)
2.4) Run Disk Management. Shrink C: partition with 10 to 15 GB extra space or even more. Create a new partition using the freed space. This partition will be used later to store the captured image. Rename Windows partition as Windows, and the new image partition as Image. Create a new folder in this new partition, name the folder as Scratch. Later on when we boot reference machine from install media to capture image with DISM command, this folder will be needed to offer DISM enough temporary working space [/SIZE]
2.5) Shut down the PC, continue from Part Four below
Part Three
Custom W10 ISO with pre-installed software, no user accounts
This method will produce an ISO image which can be compared to any original Windows 10 ISO you download from Microsoft, apart from the fact that it already contains pre-installed software according to your choice. It will also contain a customised and personalised default user profile, the base Windows uses whenever a new user profile will be created.
Customised default user profile means that whenever a new user account is created, all customisations (Start tiles, File Explorer & desktop icon and view settings, colours, wallpaper, theme, screensaver and so on will be applied to new user profile instead of Windows defaults.
Installation using this ISO will take somewhat longer than using a standard ISO because it not only contains full Windows setup, but also the pre-installed software. Notice that depending on how much space pre-installed software takes, you might not be able to burn this ISO to a standard 4.7 GB DVD disk but have to use a dual layer disk or a USB flash drive instead.
ISO created will include no user profile folders, personal user data and files.
This ISO image can be used on any hardware setup capable of running Windows and can be shared, subject to people you share the ISO with have valid licenses and / or activation keys for both Windows 10 and pre-installed software.
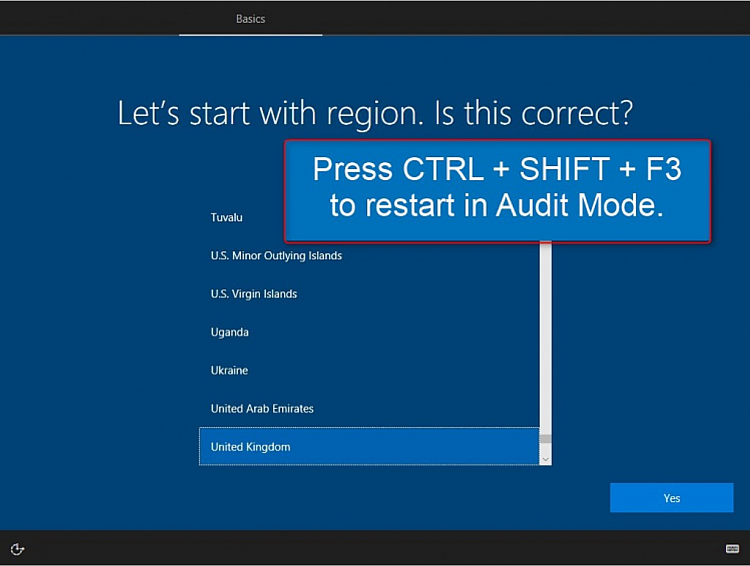
3.1) Clean install your preferred Windows 10 build on your reference machine, a Hyper-V or other virtual machine or a spare physical computer. When installation stops first time after installation to wait user input, do not click anything. Instead, press CTRL + SHIFT + F3 to restart Windows in Audit Mode:
 Alternatively follow steps 1.1 to 1.7 in Part One above, continue then from step 3.2 below3.2) Reconnect Ethernet / WiFi (physical machines) or external switch (Hyper-V virtual machines) to get Internet connection3.3) Install your preferred software, customise and personalise Windows, remove / add Start tiles as you wish (see Part Six Step 6.1), set your preferred group policies (group policies not available in Home and Single Language editions). Do not run any program you install!Notice that software installed now will be included in ISO install media, and will be pre-installed for all users on each computer you install Windows to using this custom ISO
Alternatively follow steps 1.1 to 1.7 in Part One above, continue then from step 3.2 below3.2) Reconnect Ethernet / WiFi (physical machines) or external switch (Hyper-V virtual machines) to get Internet connection3.3) Install your preferred software, customise and personalise Windows, remove / add Start tiles as you wish (see Part Six Step 6.1), set your preferred group policies (group policies not available in Home and Single Language editions). Do not run any program you install!Notice that software installed now will be included in ISO install media, and will be pre-installed for all users on each computer you install Windows to using this custom ISO3.4) Open Notepad, paste the following code to it, save it as File name: unattend.xml (exactly this name!) and Save as type: All files (important!) in C:\Windows\System32\Sysprep folder
64 bit Windows:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <unattend xmlns="urn:schemas-microsoft-com:unattend"> <settings pass="specialize"> <component name="Microsoft-Windows-Shell-Setup" processorArchitecture="amd64" publicKeyToken="31bf3856ad364e35" language="neutral" versionScope="nonSxS" xmlns:wcm="http://schemas.microsoft.com/WMIConfig/2002/State" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"> <CopyProfile>true</CopyProfile> </component> </settings> </unattend>
32 bit Windows:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <unattend xmlns="urn:schemas-microsoft-com:unattend"> <settings pass="specialize"> <component name="Microsoft-Windows-Shell-Setup" processorArchitecture="x86" publicKeyToken="31bf3856ad364e35" language="neutral" versionScope="nonSxS" xmlns:wcm="http://schemas.microsoft.com/WMIConfig/2002/State" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"> <CopyProfile>true</CopyProfile> </component> </settings> </unattend>
This so called answer file will be read for instructions when we run Sysprep (Windows System Preparation Tool) later on. This answer file is about as small as possible, the only component included in it is called CopyProfile which when set to TRUE copies all theme / desktop / Start tile and so on personalisations to default user profile, which will then be used as base profile whenever a new user profile will be created.
3.5) Sysprepping with the Generalize switch as we will soon do, with component CopyProfile set to be TRUE in answer file has a small issue or rather a small inconvenience: it leaves the last used user folders and recent files of built-in admin to end user’s Quick Access in File Explorer.
To fix this, to reset Quick Access to defaults whenever a new user signs in first time, we need to run a small batch at first logon of new user, then remove the batch file itself from user’s %appdata% so Quick Access will not be reset on any subsequent logon.
Open an elevated (Run as administrator) Notepad (Notepad must be elevated to save in system folders), paste the following code to it, save it as File name: RunOnce.bat (or any name you prefer, with extension .bat) and Save as type: All files (important!) in
%appdata%\Microsoft\Windows\Start Menu\Programs\Startup folder
echo Y|del %appdata%\microsoft\windows\recent\automaticdestinations\* del %0
The batch file explained:
- echo Y | = Pipes (sends) a letter Y to the command given after the Pipe (|) character
- del %appdata%\microsoft\windows\recent\automaticdestinations\* = Resets the Quick Access to defaults. This command expects the user to enter either Y for Yes or N for No. As the Y will be in this case piped, user interaction is not needed but instead the Y will be entered automatically
- del %0 = Deletes the batch file itself after it has been run. Leaving this away, not deleting the batch file, would reset the Quick Access every time the user signs in
3.6) Run Disk Management. Shrink C: partition with 10 to 15 GB, create a new partition using the freed space. This partition will be used later to store the captured image. Rename Windows partition as Windows, and the new image partition as Image. Create a new folder in this new partition, name the folder as Scratch. Later on when we boot reference machine from install media to capture image with DISM command, this folder will be needed to offer DISM enough temporary working space
3.7) Delete all possible downloaded software installers and imported assets from File Explorer > Quick Access > Downloads folder. Run Extended Disk Clean-up, selecting and removing everything possible (tutorial)
Hyper-V users, when disk has been cleaned create a checkpoint
3.8) In Sysprep dialog still open on your desktop, select System Cleanup Action: Enter System Out-of-Box Experience (OOBE), select Shutdown Options: Shutdown, select (tick the box) Generalize, click OK:

3.9) Sysprep will now prepare Windows, shutting down machine when done. Continue from below (Part Four):

Part Four
Capture Windows image (create custom install.wim)
Alternative method for virtual machine users, see steps 4.6 to 4.13
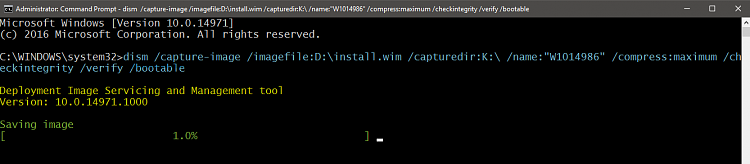
4.1) Boot the PC with Windows 10 install media. Use as recent install media as possible to ensure that DISM is most recent possible! In my case now, doing build 14986 ISO now, the most recent ISO / install media was build 14971.4.2) When you arrive the region and format selection, press SHIFT + F10 to open Command Prompt:
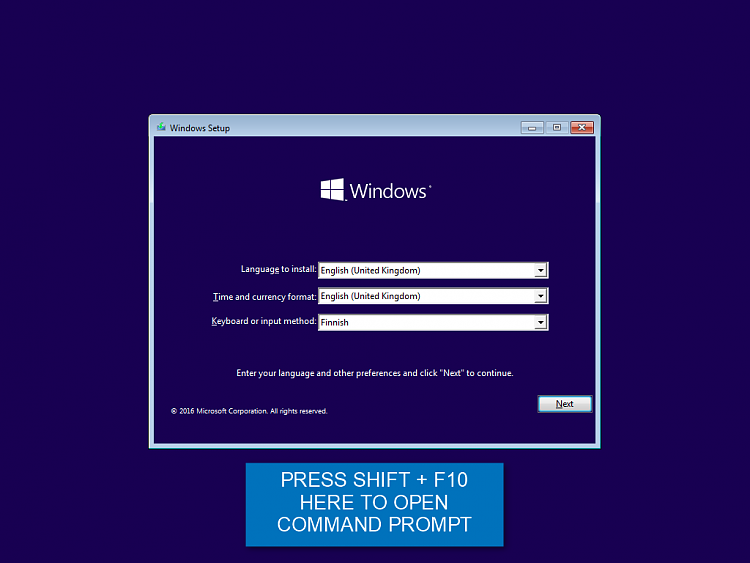 4.3) Enter command diskpart, press Enter (#1 in screenshot after step 4.4), enter command list vol (#2)This lists all volumes on your hard disks. Find the drive letters for your Windows system partition (in recovery console it’s not always C!), and for the volume (disk / partition) where you want to write (store) the new customised install.wim file. You can capture image on any internal or external disk / partition as long as it is big enough to store the captured Windows image (it will be at least 5 GB and might be as big as 20 GB, depending on software installed).In my case now it is easy because I have labeled my partitions (tutorial) with clean and understandable names. I want to capture Windows from volume D labelled as Windows and create the new install.wim in volume E labelled as Image (#3).Exit diskpart with command exit (#4).4.4) Enter the following command to create a new install.wim file (#5):
4.3) Enter command diskpart, press Enter (#1 in screenshot after step 4.4), enter command list vol (#2)This lists all volumes on your hard disks. Find the drive letters for your Windows system partition (in recovery console it’s not always C!), and for the volume (disk / partition) where you want to write (store) the new customised install.wim file. You can capture image on any internal or external disk / partition as long as it is big enough to store the captured Windows image (it will be at least 5 GB and might be as big as 20 GB, depending on software installed).In my case now it is easy because I have labeled my partitions (tutorial) with clean and understandable names. I want to capture Windows from volume D labelled as Windows and create the new install.wim in volume E labelled as Image (#3).Exit diskpart with command exit (#4).4.4) Enter the following command to create a new install.wim file (#5):dism /capture-image /imagefile:E:\install.wim /capturedir:D:\ /ScratchDir:E:\Scratch /name:"AnyName" /compress:maximum /checkintegrity /verify /bootable
In case copying the code from above CODE box is difficult, here’s the command also in QUOTE box for easier copy & paste:
dism /capture-image /imagefile:E:\install.wim /capturedir:D:\ /ScratchDir:E:\Scratch /name:”AnyName” /compress:maximum /checkintegrity /verify /bootable
Replace drive letter E in imagefile switch (green highlight in screenshot) with the drive letter and folder path of the target drive where you want your custom install.wim be written (saved), drive letter D in capturedir switch (blue highlight) with the Windows system partition, and temporarily working folder Scratch path (depending which method you chose, see either step 2.4 or step 3.6) with correct path as shown by diskpart in step 4.3:
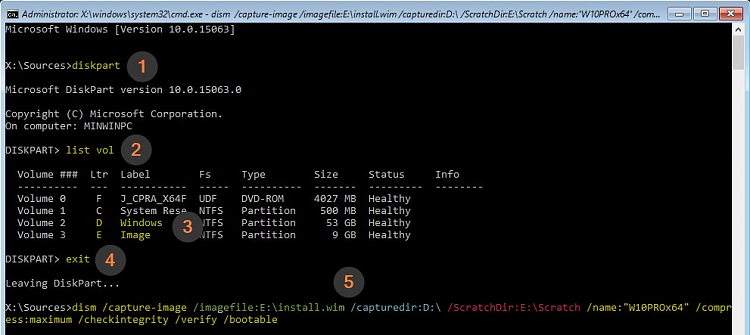
The name given in /name switch in above command is irrelevant, we will name the ISO later on. Use any name you want to.
4.5) Notice that this will take time, go get something to eat or a beer or whatever 😉
On my low end laptop this takes over 40 minutes, first half of it without any whatsoever progress indicator. On a mid level desktop it took today half an hour. DISM works somewhat faster if you don’t use optional switches /checkintegrity and /verify but I would not recommend you to create install.wim without checking its integrity and verifying it.
Don’t panic! When done, restart the reference machine normally booting to desktop and jump to Part Five
Steps 4.6 through 4.13 for virtual machine users only:
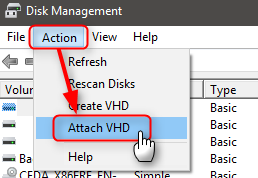
4.6) On your host machine, open Disk Management (right click Start > Disk Management)
4.7) Select Attach VHD from Action menu:
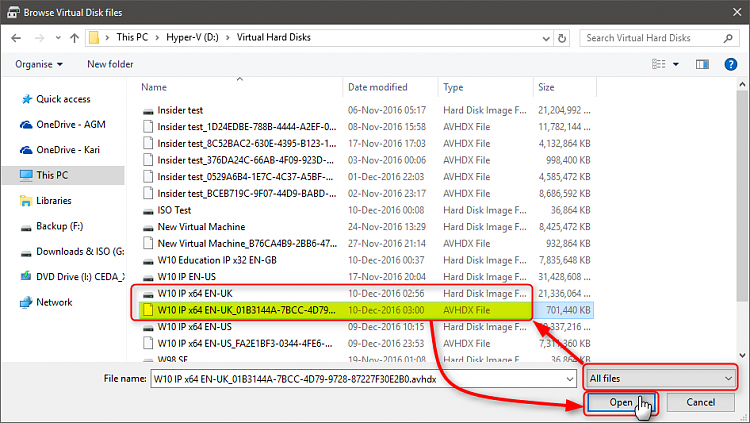
4.8) Browse to and select your reference virtual machine’s VHD / VHDX file. If you have any checkpoints (AVHD / AVHDX files) created on this vm, select the one with most recent time stamp. Notice that you have to select show all files to be able to see checkpoint AVHD / AVHDX files:
4.9) Select (tick the box) Read-only (this is very important!), click OK:
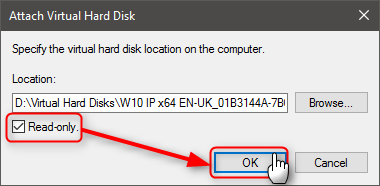
Forgetting to select Read-only will especially when mounting a checkpoint AVHD / AVHDX file make it unusable for Hyper-V; you can use it for purpose of this tutorial but not boot the vm anymore in Hyper-V.
4.10) Windows mounts the virtual hard disk, all its partitions as separate disk. In case of an MBR disk it even mounts the system reserved partition. Open the Windows system partition VHD to be sure that’s the one where Windows is installed, note the drive letter your host assigned to it:

In my case now the WIndows system partition on my reference vm when mounted on host got drive ID K:
4.11) Open an elevated Command Prompt, enter the following command to create a new install.wim file:
dism /capture-image /imagefile:D:\install.wim /capturedir:K:\ /name:"AnyName" /compress:maximum /checkintegrity /verify /bootable
In case copying the code from above CODE box is difficult, here’s the command also in QUOTE box for easier copy & paste:
dism /capture-image /imagefile:D:\install.wim /capturedir:K:\ /name:”AnyName” /compress:maximum /checkintegrity /verify /bootable
Replace drive letter D in imagefile switch (green highlight in above code box) with the drive letter and folder path of the target where you want install.wim be written, and drive letter K in capturedir switch (blue highlight) with the Windows system partition of your mounted VHD
The name given in /name switch in above command is irrelevant, we will name the ISO later on. Use any name you want to
4.12) Notice that this will take time, go get something to eat or a beer or whatever 😉
On my low end laptop this takes over 40 minutes, first half of it without any whatsoever progress indicator. On a mid level desktop it took today half an hour. DISM works somewhat faster if you don’t use optional switches /checkintegrity and /verify but I would not recommend you to create install.wim without checking its integrity and verifying it.
4.13) When done, detach the VHD / VHDX or AVHD / AVHDX file from host by right clicking it in Disk Management and selecting Detach VHD:
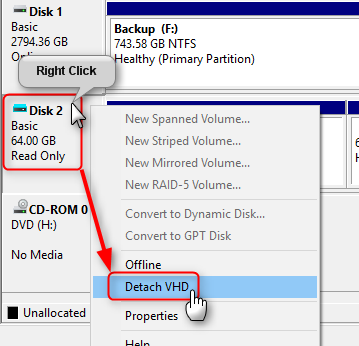
As long as the virtual hard disk remains attached to host it cannot be used in Hyper-V making vm it belongs to unbootable.
Part Five
Create a bootable ISO
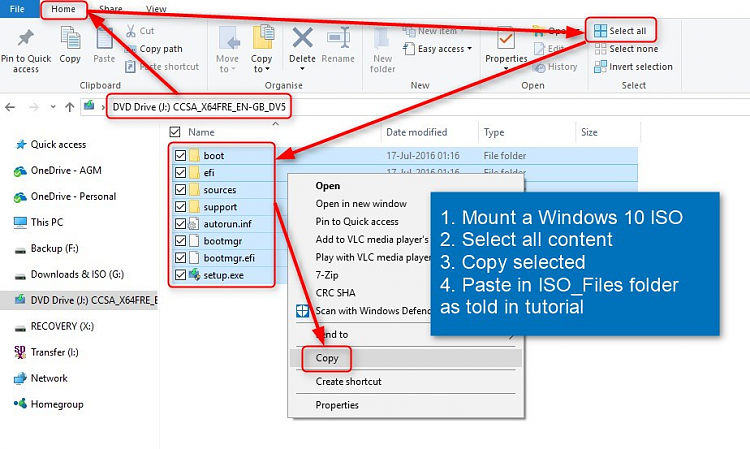 I always name this folder as ISO_Files. Alternatively copy the contents of a Windows 10 install USB or DVD to ISO_Files.5.2) Browse to your custom install.wim created earlier in Part Four. Copy it to Sources folder under ISO_Files folder, replacing the original install.wim:
I always name this folder as ISO_Files. Alternatively copy the contents of a Windows 10 install USB or DVD to ISO_Files.5.2) Browse to your custom install.wim created earlier in Part Four. Copy it to Sources folder under ISO_Files folder, replacing the original install.wim: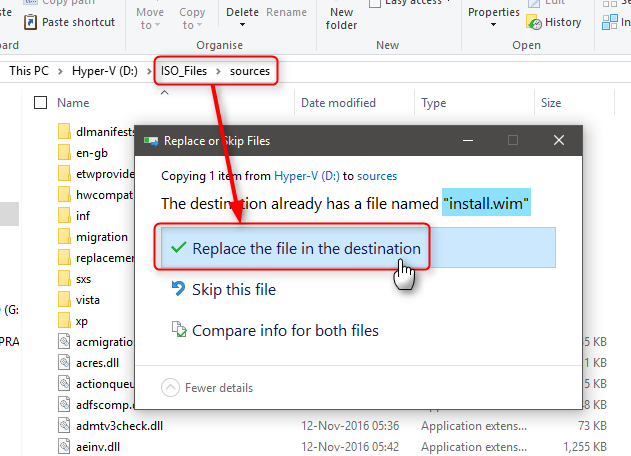
If the ISO you used in step 5.1 to get ISO files is made with Windows Media Creation Tool, the ISO_Files\Sources folder contains an install.esd file instead of install.wim.
In this case you will naturally not get “File exists” prompt. Simply delete the install.esd file and paste your custom install.wim to replace it.
5.3) If your host machine is not opted in to Insider builds, download the latest Windows Assessment and Deployment Kit (ADK) for Windows 10: Windows ADK downloads – Windows Hardware Dev Center
Windows Insider Preview ADK instead: Windows Insider Preview ADK
Full download of ADK is about 7.5 GB but luckily we only need Deployment Tools. Unselect everything else and click Install:

5.4) Start elevated (right click > More > Run as administrator) Deployment and Imaging Tools interface:
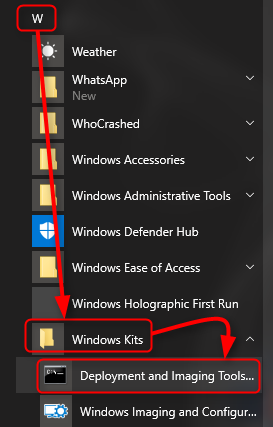
5.5) The path shown in prompt is annoyingly long. To shorten it and jump to root of drive C:, type cd\ and hit Enter. The cd command (abbreviation from Change Directory) changes the current working folder (directory), in this case to root of current drive (backslash \ = root, two dots .. = up one level).
Enter the following command:
oscdimg.exe -m -o -u2 -udfver102 -bootdata:2#p0,e,bd:\iso_files\boot\etfsboot.com#pEF,e,bd:\iso_files\efi\microsoft\boot\efisys.bin d:\iso_files d:\14986PROx64.iso
In case copying the code from above CODE box is difficult, here’s the command also in QUOTE box for easier copy & paste:
oscdimg.exe -m -o -u2 -udfver102 -bootdata:2#p0,e,bd:\iso_files\boot\etfsboot.com#pEF,e,bd:\iso_files\efi\microsoft\boot\efisys.bin d:\iso_files d:\14986PROx64.iso
Replace three instances of d:\iso_files (green highlight in above code box and screenshot) with drive and folder where you copied Windows installation files. Notice that this is not a typo: first two of these instances are typed as argument for switch -b without a space in between the switch and argument, to tell oscdimg command where to find boot files to be added to ISO.
Replace d:\14986PROx64.iso (highlighted red) with drive and path where you want to store the ISO image plus your preferred ISO file name.
Although the command seems a bit complicated, everything in it is needed. See more about oscdimg command line options: Oscdimg Command-Line Options
Part Six
Additional tips & information
6.1) If you selected method in Part Two, ISO from existing installation, note that all existing user accounts will remain intact and will be reinstated when this ISO is used for a clean install.This means that when Windows Setup (OOBE) asks you to create initial user account, setup will not accept any username already present.
To work around this, simply create a temporary user when setting up Windows after a clean install, naming it as you wish. When finally on desktop, sign out this temporary user, sign in to any existing old admin account and remove / delete the temporary user.
6.2) If you selected method in Part Three, I suggest you customise Start tiles before running Sysprep. Remove tiles not needed, add your preferred ones.
Notice that if left as is, after Sysprep when Windows is installed using your custom ISO Start needs some time to populate its default tiles. Users might see Start like this when they sign in first time:
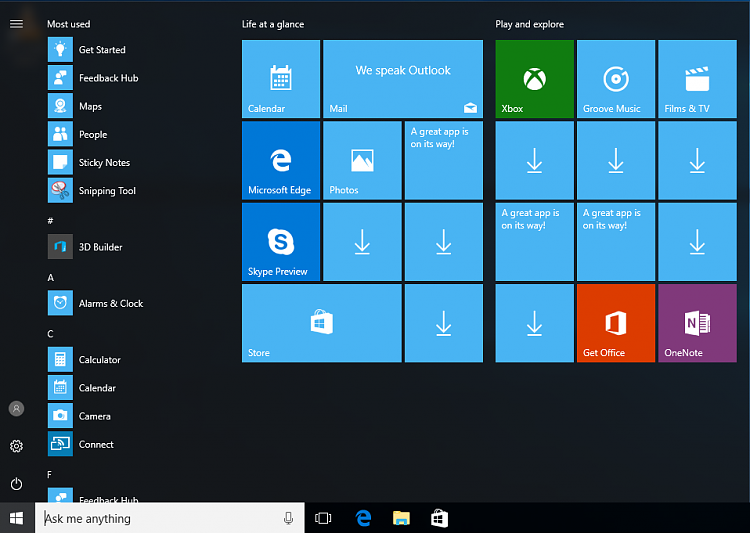
The issue is a really minor one. Half a dozen not working tiles with only a down arrow which end user can remove and replace with preferred ones, or wait until Windows populates Start correctly. Default tiles will be fully populated and functional after a restart or two.
Start will be fully functioning regardless if you customise it or not before Sysprep.
In case you want to all users to use a specific Start tile layout, modify Start as you wish before running Sysprep and export the layout in PowerShell with command
Export-StartLayout C:\Windows\System32\CustomStart.xml.
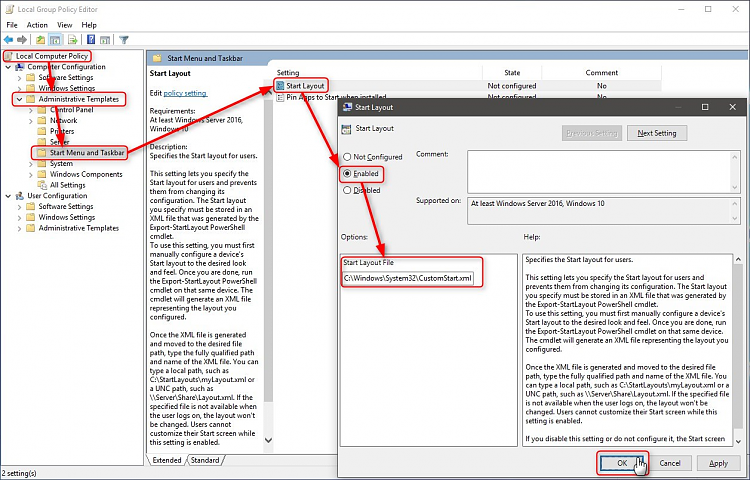
When exported, press WIN + R to open Run dialog, type gpedit.msc and hit Enter to open Group Policy Editor. On Navigation pane, browse to Local Computer Policy > Administrative Templates > Start Menu and Taskbar.
Double click Start Layout on right pane, select Enabled, enter C:\Windows\System32\CustomStart.xml in Start Layout File, click OK to save policy.
Close Group Policy Editor.
Your custom Start layout will now be forced to all user accounts.
Notice: the save location C:\Windows\System32 and filename CustomStart.xml are only my suggestions. You can save the layout file anywhere (a folder that all users have access rights) and name it as you wish (extension must be .xml).
6.3) The answer file used in Part Three Step 3.8 is the simplest possible, only to save the theme and desktop customizations to default user profile to be used in all user accounts. If you want to you can add some neat customisations. Don’t hesitate to post your questions if there’s something you’d like to include in answer file / customizations but don’t know how.
Here’s an alternative answer file for a 64 bit ISO (replace red highlighted adm64 with x86 for a 32 bit ISO):
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <unattend xmlns="urn:schemas-microsoft-com:unattend"> <settings pass="specialize"> <component name="Microsoft-Windows-Shell-Setup" processorArchitecture="amd64" publicKeyToken="31bf3856ad364e35" language="neutral" versionScope="nonSxS" xmlns:wcm="http://schemas.microsoft.com/WMIConfig/2002/State" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"> <OEMInformation> <Logo>C:\Windows\System32\oemlogo.bmp</Logo> <Manufacturer>Ten Forums</Manufacturer> <SupportHours>24/7</SupportHours> <SupportPhone>+44 123 456789</SupportPhone> <SupportURL>https://www.tenforums.com</SupportURL> </OEMInformation> <CopyProfile>true</CopyProfile> <OEMName>Ten Forums</OEMName> <RegisteredOrganization>Ten Forums</RegisteredOrganization> <RegisteredOwner>Kari</RegisteredOwner> </component> </settings> </unattend>
Let’s see first the part in <OEMInformation> tags, highlighted green in above code box (list item numbers refer to screenshot below, showing what values various answer file components set):
2.) Manufacturer
3.) Support hours, a text string. In example I’ve set it to be “24/7” but you can use any string like “MON – FRI 09 – 17”
4.) Support phone number
5.) Link to online supportAnd the blue highlighted components:
6.) Registered owner
7.) Registered organisation
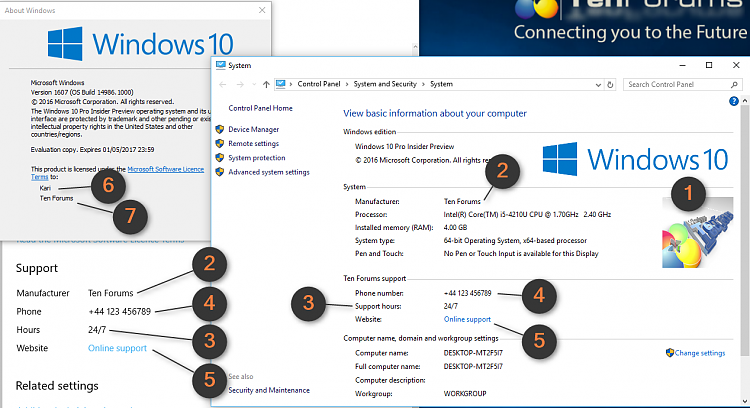
(Click to enlarge.)For more detailed instructions on creating answer files, see this tutorial: Create media for automated unattended install of Windows 10 Windows 10 Tutorials 6.3) Hyper-V users: Apply the checkpoint you made in step 1.3, 2.6 or 3.7, depending on which ISO method you chose. Next time you start the virtual machine it will start fast, going directly to desktop of your upgraded Windows 10 and is ready for the next build upgrade
You have now a custom ISO image. Burn it to a DVD or USB. The ISO is bootable both in BIOS / MBR and UEFI / GPT systems.
Kari
Related Tutorials